3.2 KiB
3.2 KiB
Network +
OSI Model
Layer 1 Bites
- Physical Layer
- It is the connects like Cat 6 RJ45 and fiber.
- Its the on and off on the cables.
Layer 2 Frames
-
Data Link Layer.
- Packagers data int frames and transmits those frames on the network.
- Layer 2 devices view networks logically.
-
MAC Address
- Media Access Control
- Physical addressing system of a device which operates on the logical topology.
- Uses a 48-bit address assigned to a network interface card.
- EX:
D2:51:F1:3A:34:65 D2:51:F1is the vendor code
-
Logical Link Control
- Provides connection services and allows acknowledgment of receipt of message.
- Is the basic form of flow control.
- Provides basic error control functions.
- Uses a check sum.
-
How communication synchronized.
- Isochronous
- Network devices use a common reference a common reference clock source and create time slots for transmission.
- Synchronous
- Network devices agree on clocking method to indicate beginning and end of frames and can use control characters.
- Asynchronous
- Network devices reference their own internal clocks and use start and stop bits
- Isochronous
-
What Devices are layer 2
- network cards
- Bridges
- Switch
- MAC Address
Layer 3 Packets
-
Network Layer
- Forwards traffic (routing) with logical address.
- IP address IPv4 IPv6
- Logical addressing
- Ip Addressing IPv4 and IPv6
- Switching (Routing)
- Route discovery and selction
- Connection Services
- Banwidth usage
- Multiplexing
-
How should data be forward or routed
- Packet Switching (Most common)
- Data is divided into packets and then forwarded to is IP address.
- Circuit Switching
- Dedicated communication link is establed between two devices.
- It uses one path when the connect establed and the whole time the connect is there.
- Message Switching
- Data is divided into messages which may be stored and then forwarded.
- Packet Switching (Most common)
-
Route Discovery and Selection
- Manually configured as a static route or dynamically through.
-
Connection Services
- Augment Layer 2 connection services to improve reliability
- Flow Control
- Packet reordering
-
Internet Control Message Protocol
- Sends error messages and operational information to an IP destination.
Ping- Trace Route
tracert
- Sends error messages and operational information to an IP destination.
-
Devices
- Routers
- Multilayer switches
-
Protocol
- IPv4
- IPv6
- ICMP
Layer 4 Segments
-
Transport Layer
-
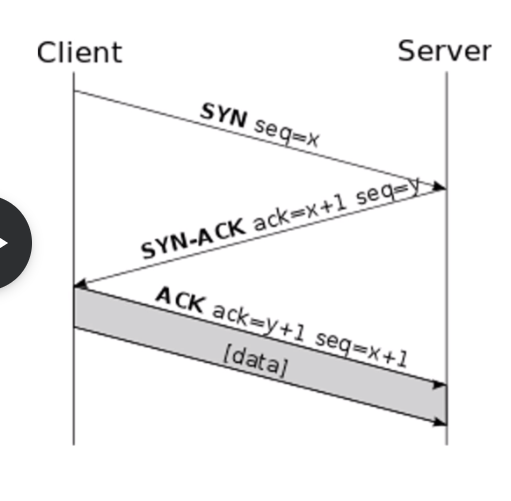
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
-
UDP User Datagram Protocol
- Connectionless protocol that is an unreliable way to transport segments across the network
-
If it dropped, Sender is unaware
-
Windowing <<<<<<< .mine * =======
-
.theirs * Buffering